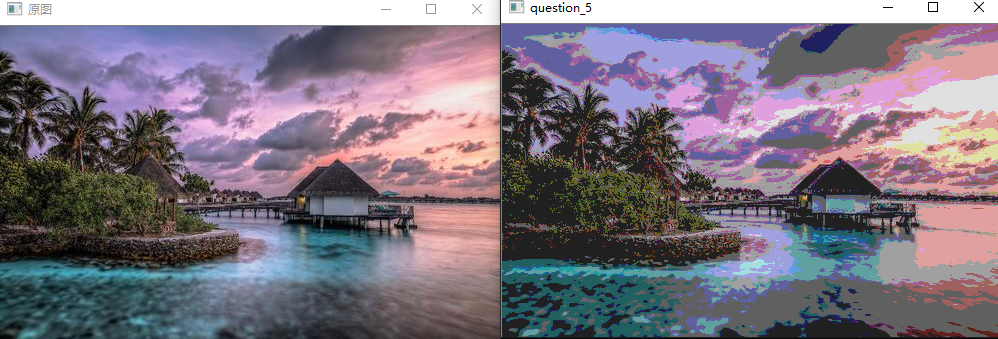
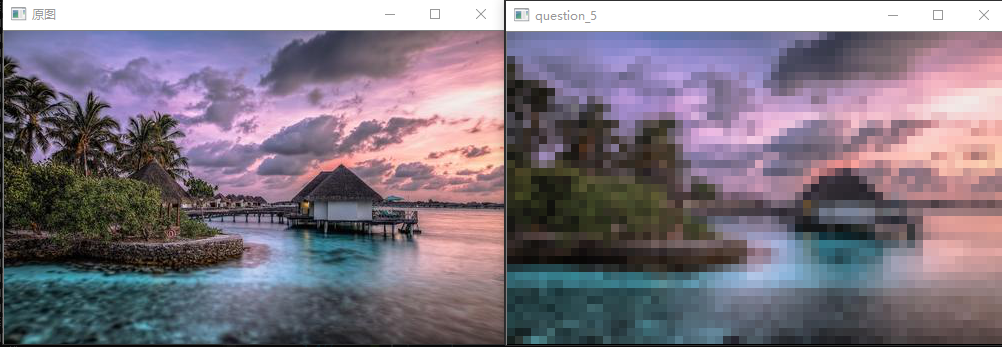
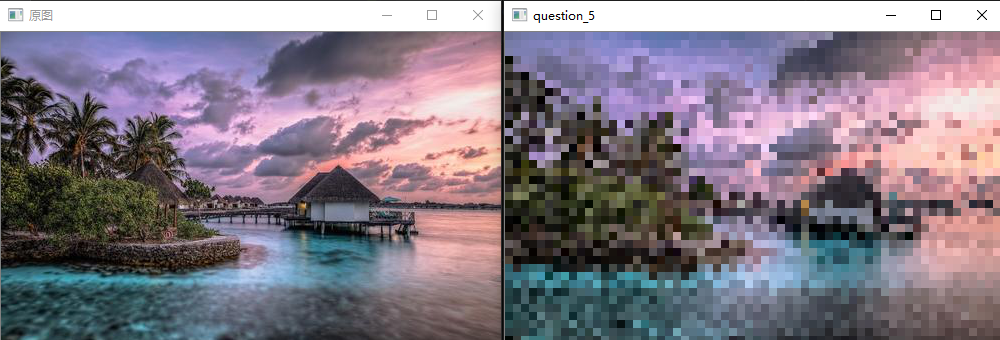
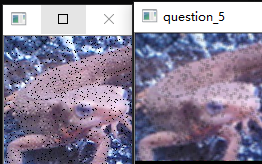
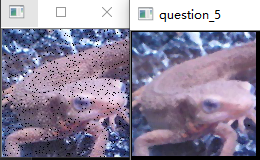
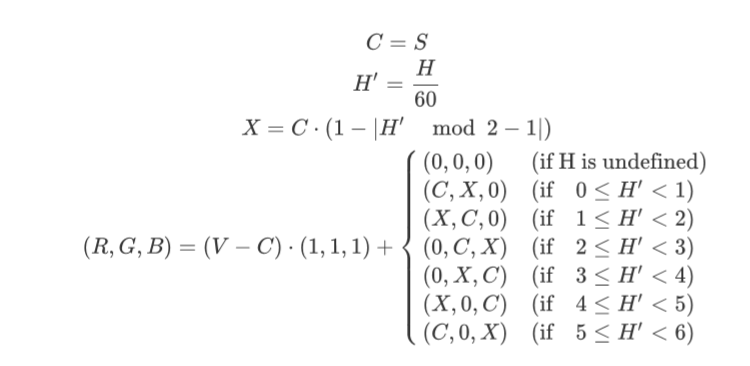问题十一至问题二十
问题十一:均值滤波器
使用$3\times3$的均值滤波器来进行滤波吧!
均值滤波器使用网格内像素的平均值。
Answer
void AvgFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst,int pad_size) {
if (!src.data) return;
int height = src.rows;
int width = src.cols;
int channel = src.channels();
dst = Mat::zeros(height+height, width+width, CV_8UC3);
for (int x = 0; x < height - pad_size; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < width - pad_size; y++) {
for (int c = 0; c < channel; c++) {
Mat pad = src(Rect(x, y, pad_size, pad_size));
int avg = sum(pad)[c] / (pad_size*pad_size);
dst.at<Vec3b>( y,x)[c] = avg;
}
}
}
}
Show

Note
- 可以使用函数
void cv::blur( InputArray src, OutputArray dst,Size ksize, Point anchor = Point(-1,-1),int borderType = BORDER_DEFAULT );j
问题十二:Motion Filter
使用$3\times3$的Motion Filter来进行滤波吧。
Motion Filter取对角线方向的像素的平均值,像下式这样定义:
$$
\left[
\begin{matrix}
\frac{1}{3}&0&0\
0&\frac{1}{3}&0\
0 & 0& \frac{1}{3}
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
Answer
void MotionFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst, int pad_size) {
if (!src.data) return;
int height = src.rows;
int width = src.cols;
int channel = src.channels();
dst = Mat::zeros(height + height, width + width, CV_8UC3);
//initPad
Mat pad = Mat::eye(pad_size, pad_size, CV_32F)/pad_size;
pad.at<float>(0, 0);
for (int x = 0; x < height-1; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < width-1; y++) {
for (int c = 0; c < src.channels(); c++) {
if (x - 1 >= 0 && y - 1 >= 0) {
for (int idx = 0; idx < pad_size; idx++)
dst.at<Vec3b>(x, y)[c] += src.at<Vec3b>(x - 1 + idx, y - 1 + idx)[c] * (pad.at<float>(idx, idx));
}
else {
dst.at<Vec3b>(x, y)[c] = src.at<Vec3b>(x, y)[c];
}
}
}
}
}
Note
- OpenCV的forEach实现采用了并行的方法,所以可以在单独使用一个像素时使用,如果使用该像素时,需要依赖旁边的其他像素,那么可能造成访问冲突
Show

问题十三:MAX-MIN滤波器
使用MAX-MIN滤波器来进行滤波吧。
MAX-MIN滤波器使用网格内像素的最大值和最小值的差值对网格内像素重新赋值。通常用于边缘检测。
边缘检测用于检测图像中的线。像这样提取图像中的信息的操作被称为特征提取。
边缘检测通常在灰度图像上进行。
Principle

我们知道,图像的细节属于低频信息,图像的边缘属于高频信息。我们使用一定大小的 Max-Min 滤波器作用于图像,当滤波器作用于图像细节时,输出结果往往趋向于0(黑色);而滤波器作用于图像边缘时,Max-Min 输出结果往往趋向于255(白色)。所以 最大-最小滤波器 能有效地用于检测图像的边缘和轮廓。
Answer
void Max_MinFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst, int pad_size) {
if (!src.data) return;
int height = src.rows;
int width = src.cols;
int channel = src.channels();
dst = Mat::zeros(height + height, width + width,CV_8UC1);
src=toGray(src);//第二问,将图像转换为灰度图像
for (int x = 0; x < height - 1; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < width - 1; y++) {
if (x - 1 >= 0 && y - 1 >= 0) {
Mat pad = src(Rect( x - 1, y - 1, pad_size, pad_size)).clone().reshape(1, 1);
Mat afterSort;
sort(pad, afterSort, CV_SORT_EVERY_ROW + CV_SORT_ASCENDING);
uchar max = afterSort.at<uchar>(0, pad_size*pad_size - 1);
uchar min = afterSort.at<uchar>(0, 0);
if (min == 0) {
std::cout << "?";
}
dst.at<Vec<uchar,1>>(y,x)[0] = max - min;
}
else {
dst.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>(y, x)[0] = src.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>(y, x)[0];
}
}
}
}
Show
- pad_size为3
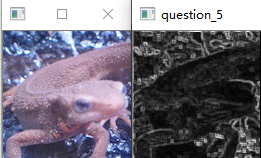
- pad_size为5

Note
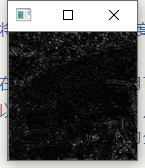
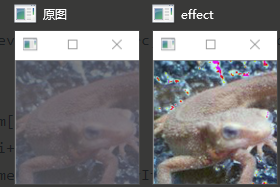
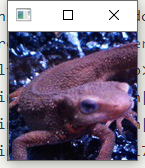
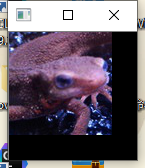
- 正如Principe所说,常用在边缘检测.虽然叫滤波器,但实际上并不能像之前的均值滤波,高斯滤波那样消除掉噪点,反而会是椒盐噪点扩大.如图:

问题十四:差分滤波器(Differential Filter)
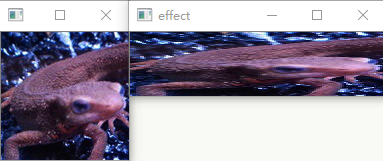
使用$3\times3$的差分滤波器来进行滤波吧。
差分滤波器对图像亮度急剧变化的边缘有提取效果,可以获得邻接像素的差值。
纵向:
$$
K=\left[
\begin{matrix}
0&-1&0\
0&1&0\
0&0&0
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
横向:
$$
K=\left[
\begin{matrix}
0&0&0\
-1&1&0\
0&0&0
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
Answer
void DifferentialFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst, int pad_size=3) {
if (!src.data) return;
int height = src.rows;
int width = src.cols;
int channel = src.channels();
dst = Mat::zeros(height + height, width + width, CV_8UC1);
src = toGray(src);
//initKernel
Mat pad = Mat::zeros(pad_size, pad_size, CV_32SC1);
pad.at<Vec<int, 1>>(0, 1) = -1;
pad.at<Vec<int, 1>>(1, 1)[0] = 1;
printMat(pad);
// filtering
for (int x = 0; x < height; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < width; y++) {
if (x - pad_size / 2 >= 0 && y - pad_size / 2 >= 0 && y + pad_size / 2 < width&& x + pad_size / 2 < height) {
Mat rect = src(Rect(x - pad_size / 2, y - pad_size / 2, pad_size, pad_size));
dst.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>( y, x)[0] =abs(rect.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>(1, 1)[0] * pad.at<Vec<int, 1>>(1, 1)[0] + rect.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>(0, 1)[0] * pad.at<Vec<int, 1>>(0, 1)[0]);
}
else {
dst.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>(x, y)[0] = src.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>(x,y)[0];
}
}
}
}
Note
Mat初始化的时候要注意每个像素的数据类型,否则会导致使用at函数时定位出现偏差.猜测内部实现原理是是通过offset*sizeof()来定位的.
矩阵数据类型:
– CV_(S|U|F)C
S = 符号整型 U = 无符号整型 F = 浮点型
CV_8UC1 是指一个8位无符号整型单通道矩阵,
CV_32FC2是指一个32位浮点型双通道矩阵
CV_8UC1 CV_8SC1 CV_16U C1 CV_16SC1
CV_8UC2 CV_8SC2 CV_16UC2 CV_16SC2
CV_8UC3 CV_8SC3 CV_16UC3 CV_16SC3
CV_8UC4 CV_8SC4 CV_16UC4 CV_16SC4
CV_32SC1 CV_32FC1 CV_64FC1
CV_32SC2 CV_32FC2 CV_64FC2
CV_32SC3 CV_32FC3 CV_64FC3
CV_32SC4 CV_32FC4 CV_64FC4
其中,通道表示每个点能存放多少个数,类似于RGB彩色图中的每个像素点有三个值,即三通道的。
图片中的深度表示每个值由多少位来存储,是一个精度问题,一般图片是8bit(位)的,则深度是8.
1--bit_depth---比特数---代表8bite,16bites,32bites,64bites---举个例子吧--比如说,如
如果你现在创建了一个存储--灰度图片的Mat对象,这个图像的大小为宽100,高100,那么,现在这张
灰度图片中有10000个像素点,它每一个像素点在内存空间所占的空间大小是8bite,8位--所以它对
应的就是CV_8
2--S|U|F--S--代表---signed int---有符号整形
U--代表--unsigned int--无符号整形
F--代表--float---------单精度浮点型
3--C----代表---一张图片的通道数,比如:
1--灰度图片--grayImg---是--单通道图像
2--RGB彩色图像---------是--3通道图像
3--带Alph通道的RGB图像--是--4通道图像
所以在内部想要保存int类型整数是,要使用CV_32S*,32代表的是Bit数,一个int是4byte,32bit
Show
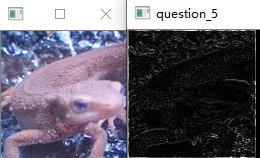
问题十五:Sobel滤波器
使用$3\times3$的Sobel滤波器来进行滤波吧。
Sobel滤波器可以提取特定方向(纵向或横向)的边缘,滤波器按下式定义:
纵向:
$$
K=\left[
\begin{matrix}
1&2&1\
0&0&0\
-1&-2&-1
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
横向:
$$
K=\left[
\begin{matrix}
1&0&-1\
2&0&-2\
1&0&-1
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
Answer
因为后面由多到题目用到给定模板进行滤波,所以编写几个函数
-
根据kernel计算需要做filter的Mat中间值
//_T 是图像的数据类型,8通道的即为Vec<uchar,1>
//_Tk是Kernel的数据类型,因为kernel中需要出现负数,所以我采用了Vec<int,1>
template<typename _T,typename _Tk>
_T& filterMul(const Mat& src, const Mat& kernal) {
_T result;
int num = 0;
if (!src.data) return result;
int height = src.rows;
int width = src.cols;
if (height != kernal.rows || width != kernal.cols) return result;//两个形状要一样
int channel = src.channels();
for (int x = 0; x < height; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < width; y++) {
_T a = src.at<_T>(x, y);
_Tk b = kernal.at<_Tk>(x, y);
num += a[0] * b[0];
}
}
if (num < 0) num = 0;
result[0] = num;
return result;
}
-
将kernel与整个图像做卷积求计算中间像素值
Mat filterConv(Mat& src, Mat& kernel) {
Mat dst;
if (!src.data) return dst;
int height = src.rows;
int width = src.cols;
int pad_size = kernel.rows;
dst = Mat::zeros(height*2, width*2, CV_8UC1);
// filtering
for (int x = 0; x < height; x++) {
for (int y = 0; y < width; y++) {
if (x - pad_size / 2 >= 0 && y - pad_size / 2 >= 0 && y + pad_size / 2 < width&& x + pad_size / 2 < height) {
Mat rect = src(Rect(x - pad_size / 2, y - pad_size / 2, pad_size, pad_size));
dst.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>( y, x) = filterMul<Vec<uchar, 1>,Vec<int,1>>(rect, kernel);
}
else {
dst.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>(x, y) = src.at<Vec<uchar, 1>>(x, y);
}
}
}
return dst;
}
-
初始化kernel
template<typename _T>
Mat initSingleChannelMat(_T* inputArray,int rows, int type) {
Mat r = Mat::zeros(rows, rows, type);
for (int i = 0; i < rows; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < rows; j++) {
r.at<Vec<_T,1>>(i, j) = *(inputArray + j + rows * i);
}
}
return r;
}
所以最后的答案长这个样子
void SobelFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst, int pad_size = 3) {
if (!src.data) return;
src = toGray(src);
//initKernel
int s[] = {
1,2,1,
0,0,0,
-1,-2,-1
};
Mat pad=initSingleChannelMat<int>(s,pad_size, CV_32SC1);
// filtering
dst = filterConv(src, pad);
}
之后的几个答案都会用到上述的几个工具函数
Show
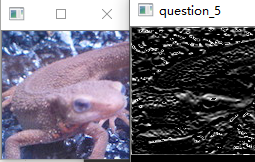
Note
- 在使用at()函数的时候,如果没有取到对应位置的值一定记得检查一下Mat的数据类型
问题十六:Prewitt滤波器
使用$3\times3$的Prewitt滤波器来进行滤波吧。
Prewitt滤波器是用于边缘检测的一种滤波器,使用下式定义:
纵向:
$$
K=\left[
\begin{matrix}
-1&-1&-1\
0&0&0\
1&1&1
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
横向:
$$
K=\left[
\begin{matrix}
-1&0&-1\
-1&0&1\
-1&0&1
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
Answer
有了上面几个工具函数,这样的问题只需要更换kernel即可
void PrewittFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst, int pad_size = 3) {
if (!src.data) return;
src = toGray(src);
//initKernel
int s[] = {
-1,-1,-1,
0,0,0,
1,1,1
};
Mat pad = initSingleChannelMat<int>(s, pad_size, CV_32SC1);
// filtering
dst = filterConv(src, pad);
}
Show
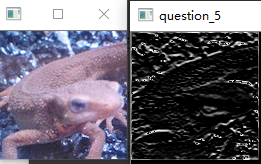
问题十七:Laplacian滤波器
使用Laplacian滤波器来进行滤波吧。
Laplacian滤波器是对图像亮度进行二次微分从而检测边缘的滤波器。由于数字图像是离散的,$x$方向和$y$方向的一次微分分别按照以下式子计算:
$$
I_x(x,y)=\frac{I(x+1,y)-I(x,y)}{(x+1)-x}=I(x+1,y)-I(x,y)\
Iy(x,y) =\frac{I(x, y+1) - I(x,y)}{(y+1)-y}= I(x, y+1) - I(x,y)
$$
因此二次微分按照以下式子计算:
$$
\begin{align*}
&I{xx}(x,y) \
=& \frac{I_x(x,y) - I_x(x-1,y)}{(x+1)-x} \
=& I_x(x,y) - Ix(x-1,y)\
=&[I(x+1, y) - I(x,y)] - [I(x, y) - I(x-1,y)]\
=& I(x+1,y) - 2\ I(x,y) + I(x-1,y)
\end{align*}
$$
同理:
$$
I{yy}(x,y)=I(x,y+1)-2\ I(x,y)+I(x,y-1)
$$
特此,Laplacian 表达式如下:
$$
\begin{align}
&\nabla^2\ I(x,y)\
=&I{xx}(x,y)+I{yy}(x,y)\
=&I(x-1,y) + I(x,y-1) - 4 I(x,y) + I(x+1,y) + I(x,y+1)
\end{align*}
$$
如果把这个式子表示为卷积核是下面这样的:
$$
K=
\left[
\begin{matrix}
0&1&0\
1&-4&1\
0&1&0
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
Answer
void LaplacianFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst, int pad_size = 3) {
if (!src.data) return;
src = toGray(src);
//initKernel
int s[] = {
0,1,0,
1,-4,1,
0,1,0
};
Mat pad = initSingleChannelMat<int>(s, pad_size, CV_32SC1);
// filtering
dst = filterConv(src, pad);
}
Show
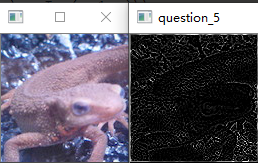
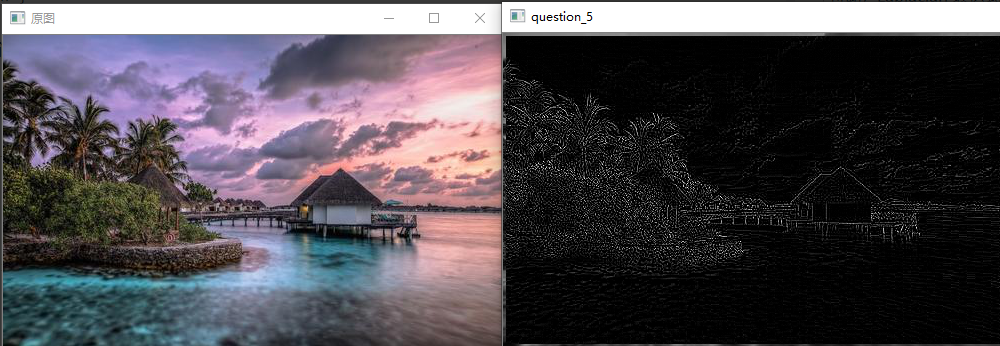
问题十八:Emboss滤波器
使用Emboss滤波器来进行滤波吧。
Emboss滤波器可以使物体轮廓更加清晰,按照以下式子定义:
$$
K=
\left[
\begin{matrix}
-2&-1&0\
-1&1&1\
0&1&2
\end{matrix}
\right]
$$
Answer
void EmbossFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst, int pad_size = 3) {
if (!src.data) return;
src = toGray(src);
//initKernel
int s[] = {
-2,-1,0,
-1,1,1,
0,1,2
};
Mat pad = initSingleChannelMat<int>(s, pad_size, CV_32SC1);
// filtering
dst = filterConv(src, pad);
}
Show
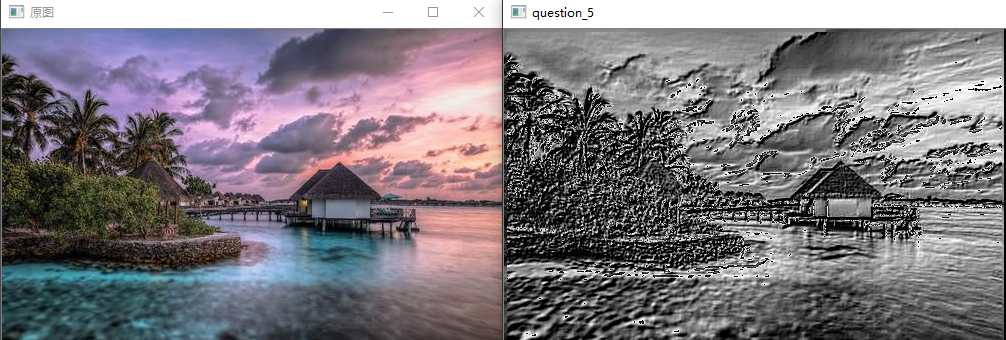
问题十九:LoG滤波器
使用LoG 滤波器,来对imori_noise.jpg检测边缘吧!
LoG即高斯-拉普拉斯(Laplacian of Gaussian)的缩写,使用高斯滤波器使图像平滑化之后再使用拉普拉斯滤波器使图像的轮廓更加清晰。
为了防止拉普拉斯滤波器计算二次微分会使得图像噪声更加明显,所以我们首先使用高斯滤波器来抑制噪声。
LoG 滤波器使用以下式子定义:
$$
\text{LoG}(x,y)=\frac{x^2 + y^2 - s^2}{2 \ \pi \ s^6} \ e^{-\frac{x^2+y^2}{2\ s^2}}
$$
Answer
void LoGFilter(Mat src, Mat& dst, int pad_size = 3) {
if (!src.data) return;
GaussianFilter(src, dst, 3, 10);
Mat newSrc = Mat(dst);
LaplacianFilter(newSrc, dst);
}
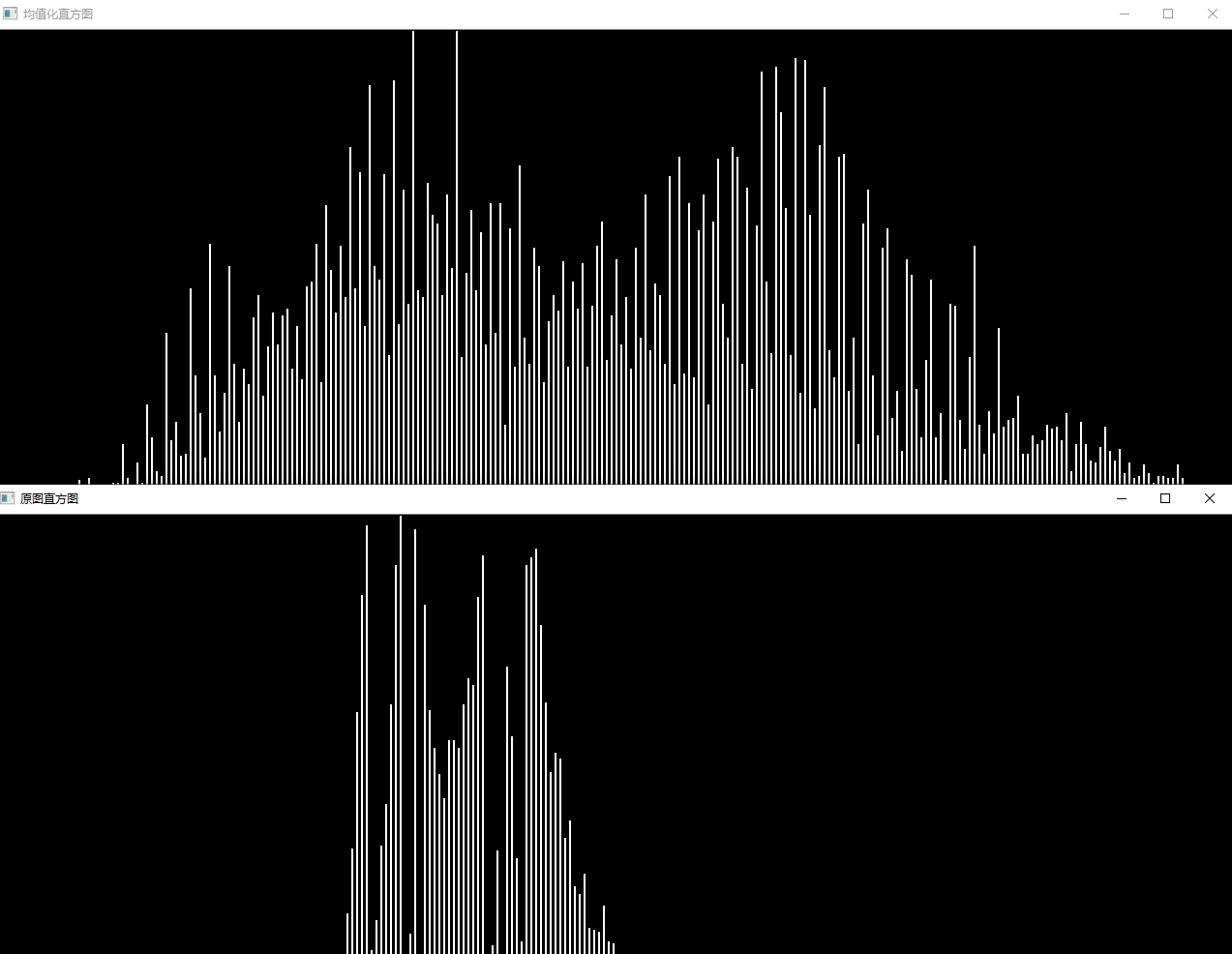
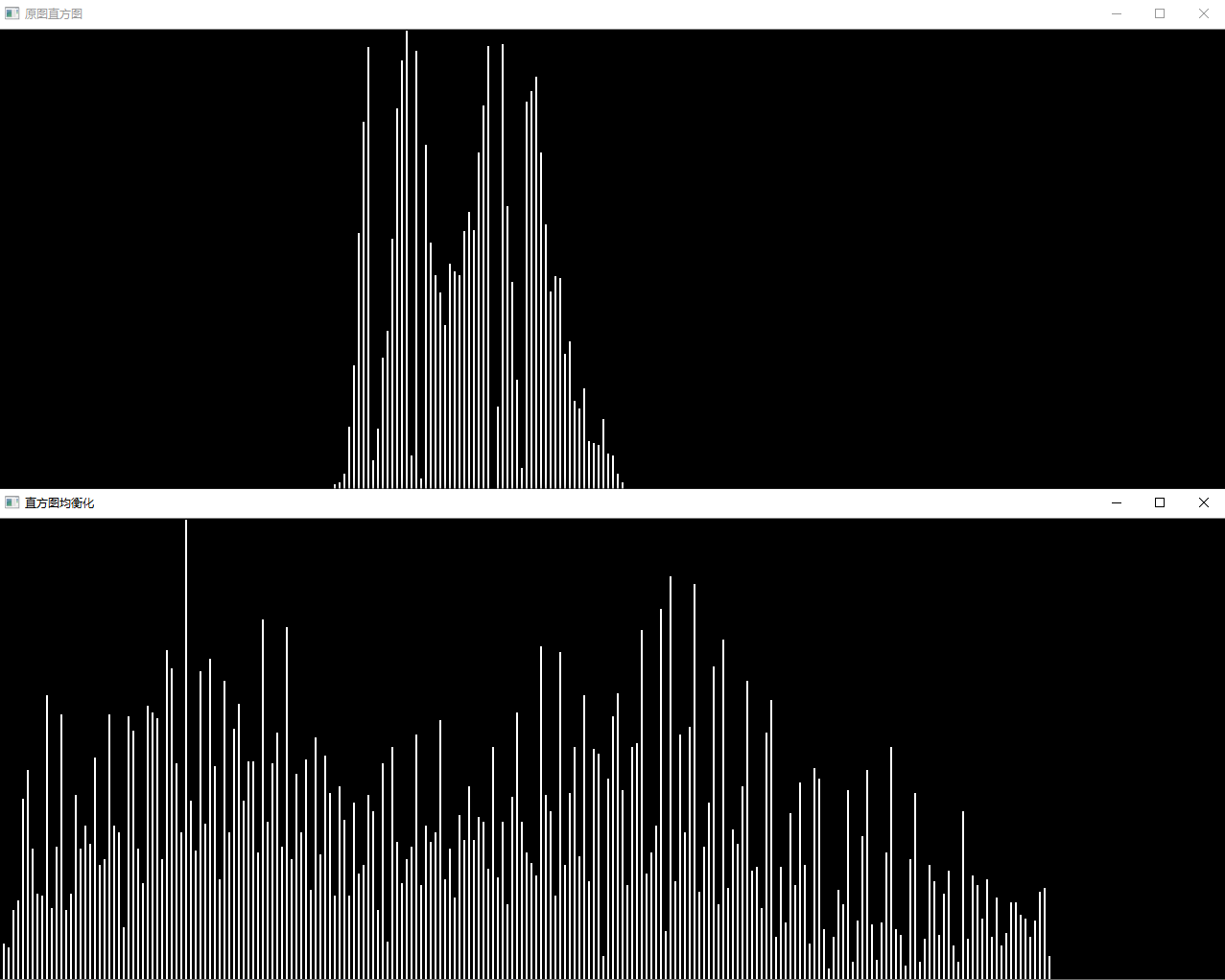
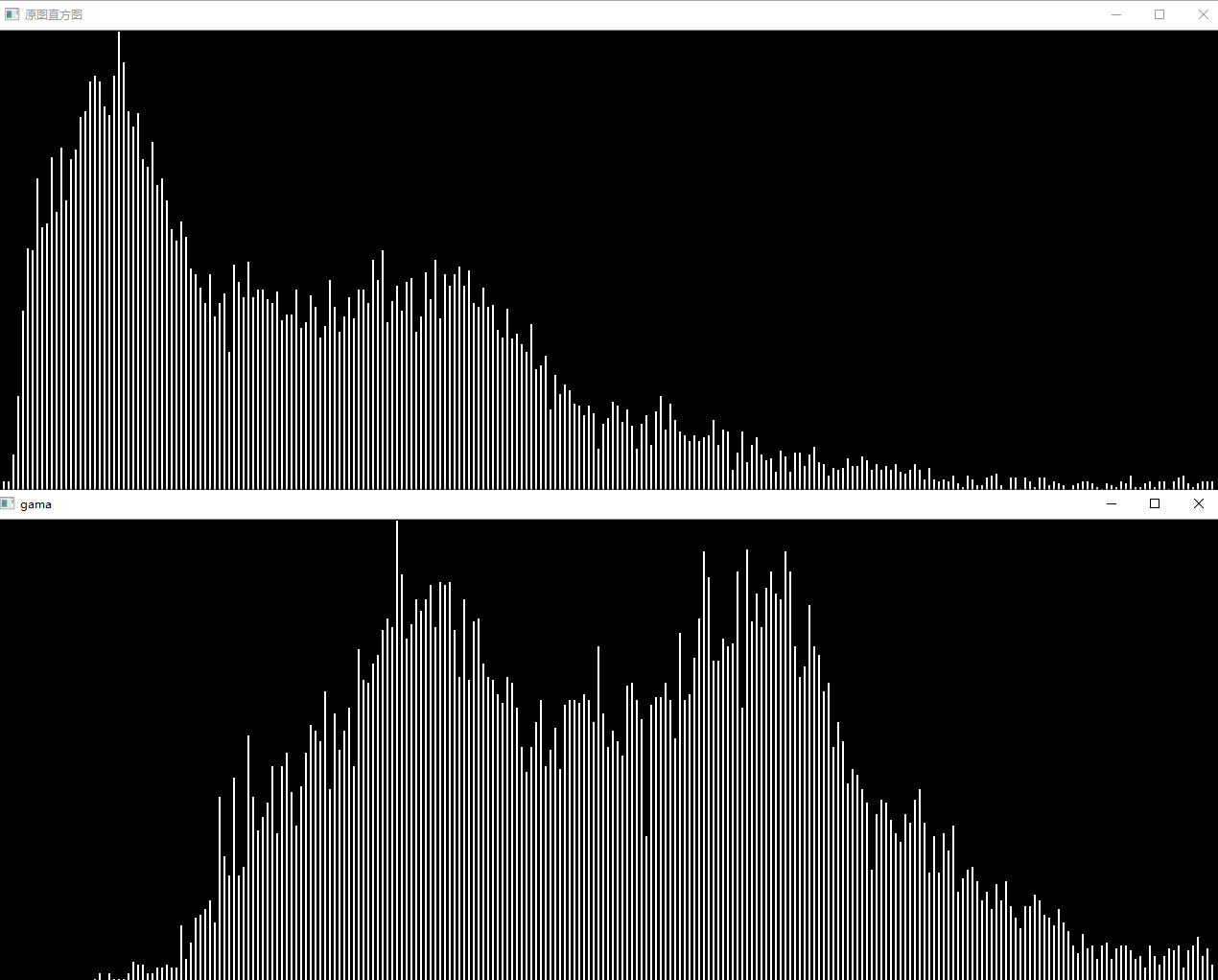
问题二十:直方图
使用Matplotlib来绘制imori_dark.jpg的直方图吧!
直方图显示了不同数值的像素出现的次数。在Matplotlib中有hist()函数提供绘制直方图的接口。
Answer
C++并没有可以直接绘制直方图的工具,所以利用Mat自己写了一个
/*
绘制直方图
*/
template<typename _T>
void paintHistogram(std::vector<_T> t,int height=480,int colWidth=5) {
Mat m = Mat::zeros(height, t.size() *colWidth, CV_8UC3);
_T maxItem = *std::max_element(t.begin(), t.end());
Vec3b color = Vec3b(255, 255, 255);
for (int item = 0; item < t.size(); item++) {
int cur_height = ((float)t[item] / (float)maxItem)*height;
for (int x = item * colWidth; x < (item + 1)*colWidth-3; x++) {
for (int y = height-1; y >height-cur_height; y--) {
m.at<Vec3b>( y,x)[1] = color[1];
m.at<Vec3b>(y, x)[0] = color[0];
m.at<Vec3b>(y, x)[2] = color[2];
}
}
}
imshow("Histogram", m);
}
有了上述工具绘制直方图就很简单
void paintGrayHistogram(Mat src) {
Mat gray = toGray(src);
std::vector<uchar> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 256; i++) {
v.push_back(0);
}
gray.forEach< Vec<uchar, 1>>([&](Vec<uchar, 1> pix, const int* position) {
v[pix[0]] += 1;
});
paintHistogram(v);
}
Show
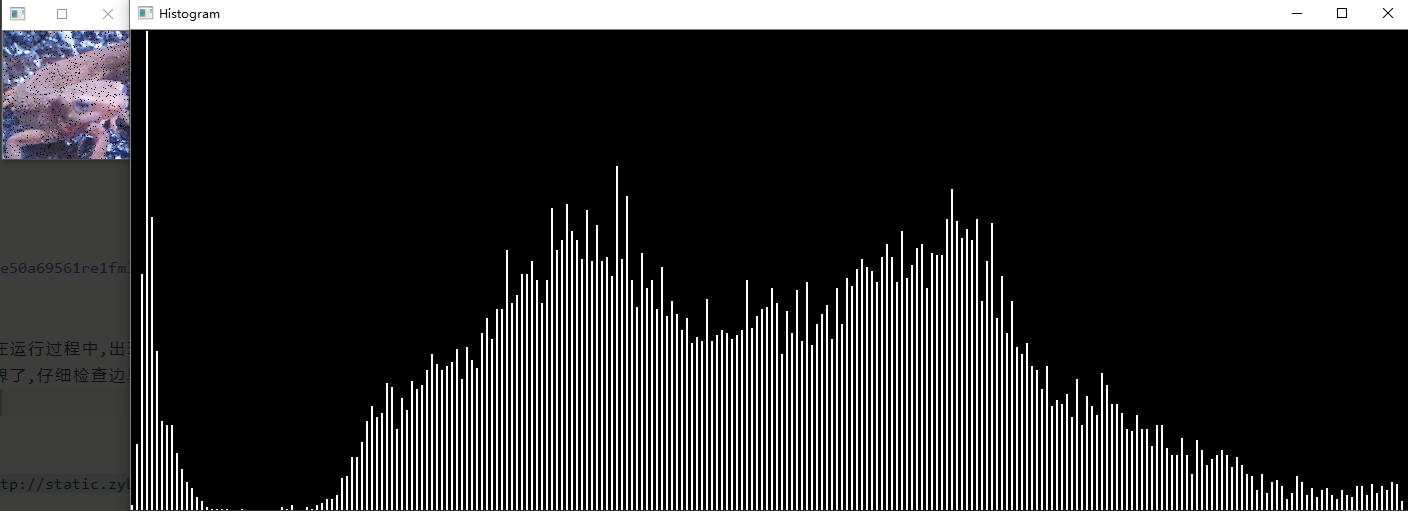
Note
- 如果在运行过程中,出现图像展示时发生"堆已损坏","无法访问0xFFFFFF"之类的,很有可能是在给Mat赋值是越界了,仔细检查边界条件,看看是不是在位于width,和height的位置赋了值,x,y要小于等于width-1,height-1






](http://static.zybuluo.com/sliverp/xjivqmgypuebpq9gytx6dz3k/image_1e5fit42n12j1ghj1as76et1eh62g.png)